How long will it take for my injury to recover?
The recovery of a operation or a injury can feel like an eternity. How long it takes to fully recover from an injury depends on several factors and is a common question from our patients. Our bodies are sometimes amazing at healing, but also at adjusting when the prospect of full recovery is questionable or no longer possible. This takes time, and in most cases there are no quick fixes. The recovery time depends on which tissue is damaged in combination with other factors such as; age, fitness, nutrition, stress and other similar influences. In this blog, we take you through the big picture and outline what you can expect in relation to your own situation.

The stages of recovery
Before going into the specific images, we need to talk about tissue repair. Tissue repair or healing is the process by which damaged tissue in the body is repaired and restored. This repair process is essential for maintaining normal functions in the body after damage or injury. This damage can occur as a result of, for example, a sports injury(external forces) or as a result of an internal process such as an inflammatory reaction due to an autoimmune disease, for example.
The process of healing consists of 3 different phases; the inflammation phase, proliferation phase and remodelling phase.
The ignition phase
This is the phase immediately after the injury occurs. The body's natural reaction is to start the inflammatory process. This defence reaction is meant to remove affected cells and start the healing process. The first phase is characterised by symptoms such as swelling, redness, pain and warmth. This phase lasts on average up to a maximum of 7 days after the onset and is sometimes even subdivided into the acute and late inflammatory phases.
A classic example of this is through your only go during exercise. Swelling, pain and loss of function occur almost soon after or at least within 24 hours.
Proliferation phase
After the inflammation phase, the proliferation phase begins. After the old cells are removed, new cells are created to replace or repair the damaged tissue. Blood vessels grow to supply oxygen and nutrients to the tissue. You can think of it as a kind of first aid for accidents. These new cells act as a kind of scar tissue and are the body's first solution to further recovery. This phase starts approximately from 1 week to 3 weeks after the onset of injury.
Remodelling phase
This is the final stage of recovery. The newly formed cells are gradually restructured. Thus, the scar tissue eventually becomes functional again and eventually stronger. These structures do not become completely like new but have the same function as the original tissue. This phase starts approximately after week 3 and can last up to 1 year or even longer.
The factors that affect tissue repair are
The blood supply to the affected area. The better the blood supply the more favourable this is for full recovery. An example of this is the meniscus, the meniscus consists of three different zones, which are categorised as well-perfused, moderately-perfused or poorly-perfused. When there is a tear in the meniscus, we see that recovery is often very dependent on the location of the tear in the meniscus.
Overall health greatly affects how quickly the body recovers
We know that things like smoking greatly reduce blood flow to the body and, as a result, people who smoke have a much longer recovery time than those who do not. Excess weight also often plays a role indirectly because fat cells release inflammatory mediators of their own by certain hormones. Now, an inflammatory phase is a normal reaction and even necessary for recovery, it is only when the symptoms of this inflammatory reaction persist that it greatly affects the recovery process. Because of that there will probably be more pain we see that this pain starts to interfere with the rehabilitation process. Nutrition can also contribute to favourable recovery. Proteins in particular are essential for tissue repair but essential fatty acids also help manage the inflammatory response. Supplements can help but are often insufficient when your normal diet is not in order.
Influences of medication on injury recovery. We know that some medications have an adverse effect on the recovery process.
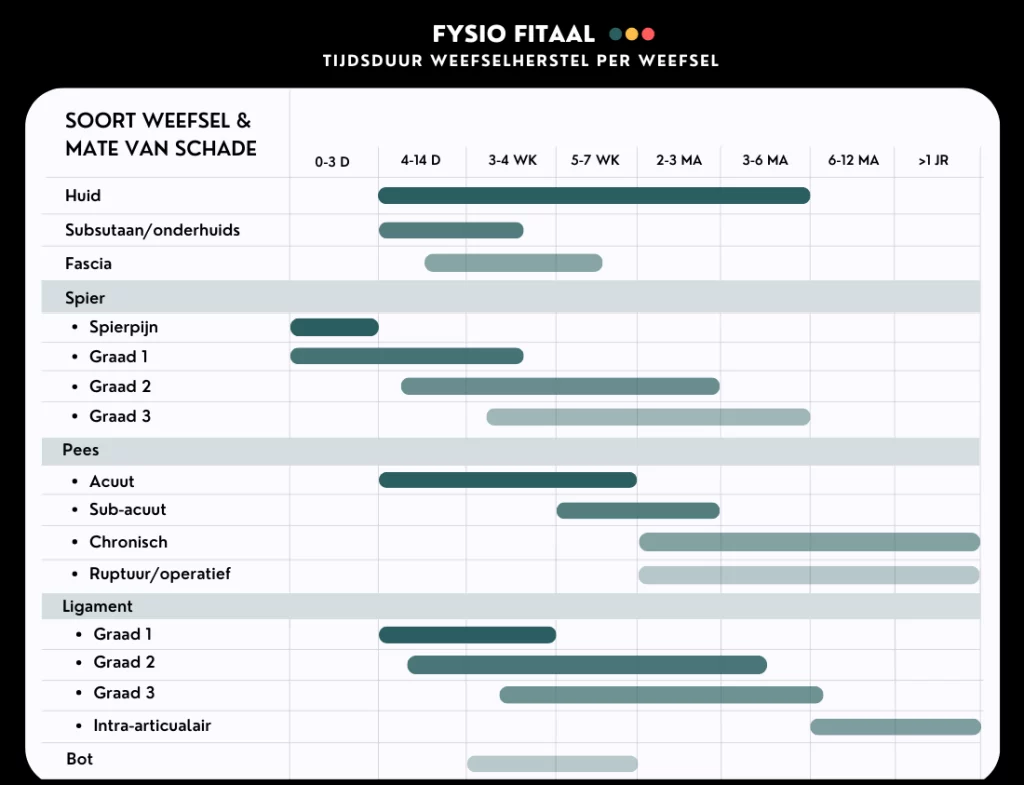
Recovery time of different tissue types
Tissues are made up of different types of cells and therefore do not all have the same recovery time. Tissues in our body can be classified into:
- Muscle
- Tendon
- Ligament
- Bot
And these structures are all made up of collagen, elastin, proteoglycans and cells. Only the proportion of these cells in the tissue is different. On the contrary, tendon tissue should be stiff and strong compared to muscle tissue. For this reason, a tendon consists proportionally much more of collagen tissue than muscle tissue. It is therefore essential to know which tissue has been damaged to create the right expectations.
Muscle tissue
More than 400 muscles enable a person to walk, run, jump and move. Sometimes these muscles get overloaded leading to a muscle injury. A muscle injury is generally classified into several categories. Whereby muscle pain due to sports is the mildest variant and a complete muscle tear is the most severe variant. In some cases, surgery is necessary to repair the tissue, which of course negatively affects recovery.
Recovery time: 2 to 12 weeks.
Tendon tissue
Tendons connect muscles to our bones and transmit forces produced by muscles. Damage to the tendon can result from overuse, but in some cases it is also due to ageing. A natural process again which comes with ageing just like grey hair or wrinkles of the skin. Our bodies are just as susceptible to ageing on the inside as we are on the outside.
Recovery time: 3 months to 1 year
- Tendinitis: 3 weeks to 2 months
- Tendinosis: 3 to 6 months
- After surgery: 3 months to 1 year
Ligaments
These structures are very similar to tendon tissue. Ligaments connect bones and provide passive stability in a joint. They provide guidance but also inhibition to extreme range of motion so that injuries can be prevented. But in some cases, they can fail in their function and become damaged. An example of a ligament is, for example, the anterior cruciate ligament or the outer ligament of the ankle. In the case of a anterior cruciate ligament injury surgery may be necessary to repair the ligament again. Other damage can sometimes still recover naturally because of the fibrous nature of the ligamentous structures. If, despite the damage, these are short enough together, repair is still possible.
Recovery time: 2 weeks to 15 months
Ligament damage: minor damage or a strain can take 2 weeks to 3 months. If surgery is necessary, the total healing process can take up to 15 months, depending on which ligament.
Bones
Bones give support to our body and serve as attachment points for ligaments and tendons. Breaking a bone is not uncommon and can occur after a fall or other high-speed accident. We do have more than 200 bones in our body. Larger bones often take longer to recover when broken.
Recovery time: 3 months to 1 year
Minor fractures such as stress fracture, for example, can heal within 3 weeks. Even in this case when surgery is necessary to repair the fracture, the recovery process can take longer than 1 year. We also see that along with a bone fracture, there is also a lot of damage in the anatomical structures that are adjacent. Which can also damage tendon tissue or ligaments.
Why physiotherapy?
Reduce recovery time with physiotherapy! Our physiotherapists are experts in treating complaints of these tissues. Our physiotherapy practice is fully equipped to rehabilitate orthopaedic complaints(muscle, tendon, ligament, bone). Rehabilitation at Fysio Fitaal in Tilburg will contribute to recovery and lasting results.
The benefits of Physiotherapy during rehabilitation:
- Reduces pain
- Increases muscle strength around the injury
- Improves mobility and agility
- The right information on the symptom picture but most importantly on expectations
- Reduces the risk of complications