FAI Impingement
In FAI impingement, the hip joint does not function as it should because the neck of the femoral head runs against the edge of the hip socket. Impingement can be freely translated as entrapment , this entrapment causes hip pain. There is a classification depending on where the problem is located. FAI stands for femoroacetabular impingement, femur is the head of the hip and the acetabulum is the socket of the hip. The extra bone growth in impingement can damage the labrum. In addition, the extra bone growth can cause accelerated wear of the hip joint, better known as osteoarthritis. Extra bone growth in places where it shouldn't be naturally causes the joint to run less smoothly. This can cause reduced mobility and restrictions in daily life. The reduced movement may be accompanied by pain symptoms. For proper assistance with FAI impingement, Fysiofitaal Tilburg is the right place to be!

Cause of hip impingement
The hip is a ball-and-socket joint and consists of a head and a socket that fit closely together. For the hip joint to move properly, the hip head slides into the hip socket. In FAI impingement, the hip joint does not move as it should because the neck of the hip head runs against the edge of the hip socket. FAI stands for Femoro Acetabular Impingement. This basically means that the femur and hip socket do not move smoothly in relation to each other. Depending on where the problem is located, there is a classification, namely CAM or Pincher.
Diagnosis of FAI hip
Extra bone growth in places where it should not be makes the joint's range of motion less good. This can cause reduced mobility and limitations in daily life. The reduced movement may be accompanied by pain symptoms.
To diagnose FAI impingement, the physiotherapist starts with an interview, also known as anamnesis. From these questions, the physiotherapist can extract a lot of information and arrive at a preliminary diagnosis. To confirm this diagnosis, the physiotherapist will perform a number of tests. Fai impingement can be recognised perfectly well by a physiotherapist and the diagnosis is therefore also easy to make.
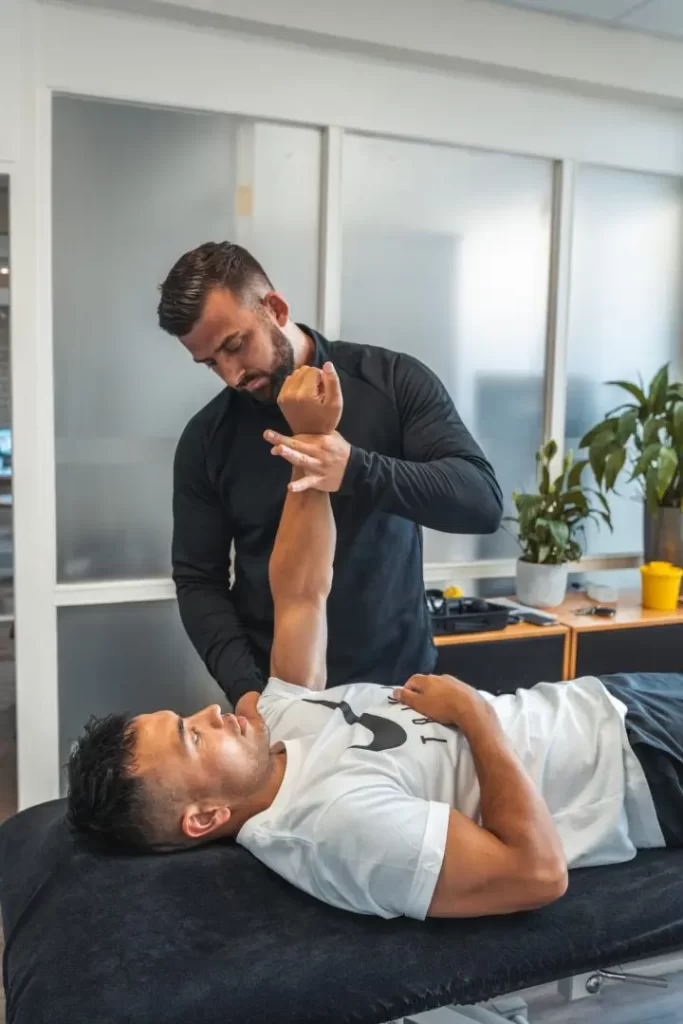
Treatment of hip pain Physio Fitaal Tilburg
Are these complaints recognisable or suffer from other complaints in the hip? Then make an appointment now at one of our therapists.
Cam Impingement
- Anatomical features: Cam impingement is caused by an abnormality in the shape of the femur (thighbone). Specifically, there is a flattening or bulge on the head-neck transition area of the femur.
- Effect on the joint: This deformity can cause, when the hip is moved, the abnormal bone to contact the edge of the hip socket, which can cause damage to the labrum (the lip of the hip socket) and cartilage.
- Most affected persons: Cam impingement is more common in young men, especially those who are active or play sports.
Pincer Impingement
- Anatomical features: Pincer impingement is caused by an abnormality or over-coverage of the hip socket (acetabulum). This may be because the hip socket is too deep or because the edge of the hip socket protrudes too far over the femur.
- Effect on the joint: In pincer impingement, the hip socket compresses the femur, leading to compression of the labrum and cartilage. Unlike cam impingement, where the damage occurs mainly on the side of the hip socket, in pincer impingement the damage is more localised on the front of the hip socket.
- Most affected persons: Pincer impingement is seen more often in middle-aged women, especially those who are active or play sports.
Combined (Cam and Pincer) Impingement
- It is also possible for a person to have both cam and pincer impingement, meaning there is a problem with both the shape of the femur and the hip socket. This is called mixed impingement and can make symptoms and treatment more complex.
Treatment of FAI, whether cam, pincer or a combination of both, can range from physiotherapy and activity modification to surgery, depending on the severity of symptoms and the patient's specific needs. It is important that a qualified healthcare provider makes an accurate diagnosis and prepares a treatment plan.
What is the labrum?
The labrum is a cartilage ring located in the hip socket. The extra bone growth in impingement can damage the labrum. In addition, the extra bone growth can cause accelerated wear of the hip joint, better known as osteoarthritis. The labrum is an important part of the hip joint. It plays an important role in the stability of the joint. More detailed information about the labrum is given below:
- Anatomical Position: The labrum is a ring of firm but flexible cartilage that sits around the edge of the hip socket (acetabulum).
- Structure: The labrum is fibrocartilaginous, meaning it is a mixture of fibrous tissue and cartilage. It is firm but also elastic.
Making an appointment at FysioFitaal
We work from multiple locations in Tilburg, always close by for professional and accessible physiotherapy. Fill in the contact form and we will contact you soon. Together, we will work on your recovery!